BenchMarking app for iPhone and iPad
Developer: APPSKOUSIKA SOTWARE DEVELOPERS (OPC) PRIVATE LIMITED
First release : 25 Nov 2014
App size: 924 Kb
Benchmarking is a systematic method by which organisations can measure themselves against the best industry practices.The essence of benchmarking is the process of borrowing ideas and adapting them to gain competitive advantage.It is tool for continuos improvement.
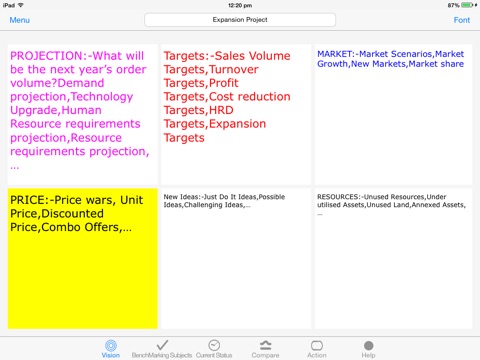
Vision &Subjects for BenchMarking(To decide what to Benchmark):-
Benchmarking can be applied to virtually any business or production process.Improvement to best in class levels in some areas will contribute greatly to market and financial success.Most organisations have a strategy that defines how the firm wants to position itself and compete in the marketplace.This strategy is usually expressed in terms of mission and vision statements. Supporting these statements is a set of critical activities,that are often referred to as critical success factors.In general,when deciding what to benchmark,it is best to begin by thinking about the mission and critical success factors.
Some questions that can be raised to decide high impact areas to benchmark are:-
1.What processes are causing most trouble?
2.How to differentiate our organisation from the competition?
3.Who contribute most to customer satisfaction?
4.Where are the loop holes?
5.Why there is a shortage?
6.When do we fail?
In deciding what to benchmark,it is best not to choose too large a scope.A benchmarking study should be done quickly.
Current Status(Understanding current Performance):-
To compare practices to outside benchmarks,it is first necessary to thoroughly understand and document the current status.
Strengths: characteristics of the subjects for benchmarking that give it an advantage over others
Weaknesses (or Limitations): are characteristics that place subjects for benchmarking at a disadvantage relative to others
Opportunities: external chances to improve performance (e.g. make greater profits) in the environment
Threats: external elements in the environment that could cause trouble for subjects for benchmarking.
Compare:-
Compare your subjects for benchmarking with the corresponding subjects of other World class/Country-wide/Industry-wide/Competitor/Other departments(Internal).Find the gaps in the performance or status.
Action:-
PLAN
Establish the objectives and processes necessary to bridge the gaps in the performance or status found in the previous step(Compare). When possible start on a small scale to test possible effects.
DO
Implement the plan, execute the process, make the change/new product/new service. Collect data for charting and analysis in the following "CHECK" and "ACT" steps.
CHECK
Study the actual results (measured and collected in "DO" above) and compare against the expected results (targets or goals from the "PLAN") to ascertain any differences. Charting data can make this much easier to see trends over several PDCA cycles and in order to convert the collected data into information. Information is what you need for the next step "ACT".
ACT
Request corrective actions on significant differences between actual and planned results. Analyse the differences to determine their root causes. Determine where to apply changes that will include improvement of the process or product. When a pass through these four steps does not result in the need to improve, the scope to which PDCA is applied may be refined to plan and improve with more detail in the next iteration of the cycle.